CCN Estimation from Space
This research focuses on estimating Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) concentrations using space-borne lidar data.
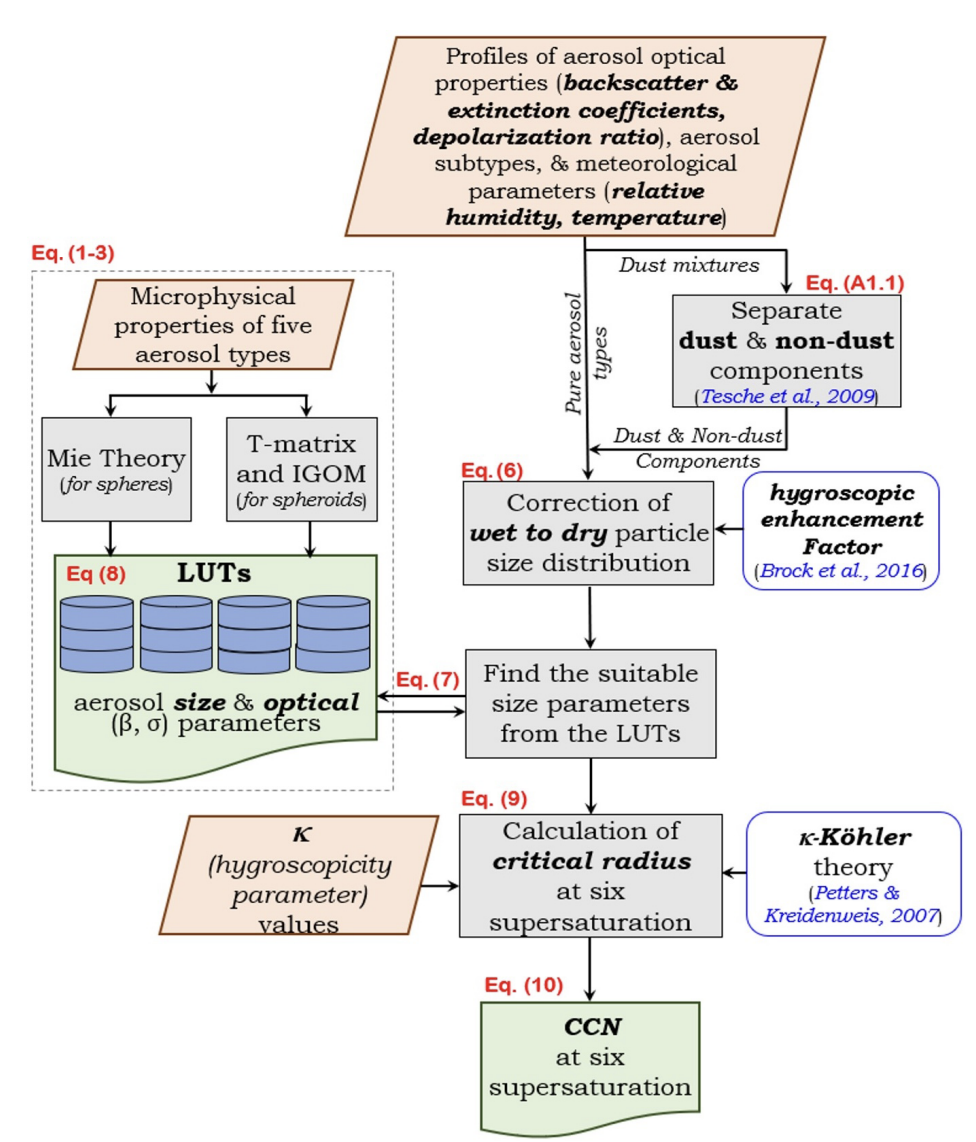
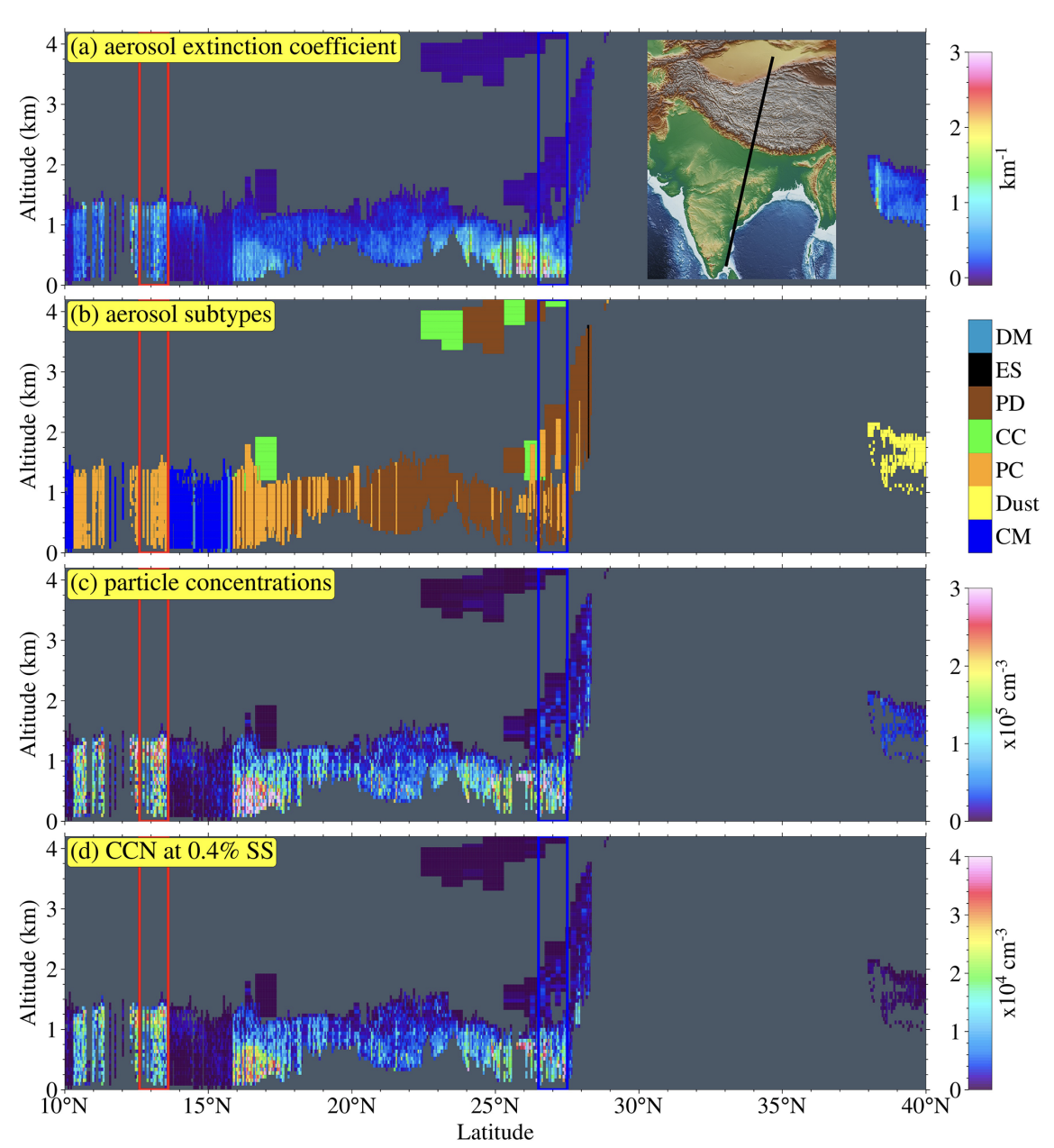
This paper presents a novel remote sensing algorithm designed to accurately measure cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) concentrations at different altitudes using data from airborne and spaceborne lidar systems. By providing vertically resolved CCN profiles, the study enhances our understanding of cloud formation processes and their impact on climate. This breakthrough allows for more precise climate modeling and better predictions of weather patterns, offering valuable insights for both scientific research and practical applications in meteorology and environmental monitoring. The algorithm represents a significant advancement in atmospheric science, enabling more detailed and accurate observations of cloud microphysics.
Key Points:
- Innovative Algorithm: A new remote sensing algorithm for vertically resolved CCN measurement using lidar data.
- Improved Climate Models: Enhances understanding of cloud formation, leading to better climate predictions.
- Atmospheric Science Advancement: Offers a powerful tool for precise cloud microphysics observation.
Journal Articles
 A remote sensing algorithm for vertically resolved cloud condensation nuclei number concentrations from airborne and spaceborne lidar observationsAtmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2024
A remote sensing algorithm for vertically resolved cloud condensation nuclei number concentrations from airborne and spaceborne lidar observationsAtmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2024- ERCCloud condensation nuclei characteristics at the Southern Great Plains site: role of particle size distribution and aerosol hygroscopicityEnvironmental Research Communications, 2021