India's Smog Crisis
This research focuses on estimating Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) concentrations using space-borne lidar data.
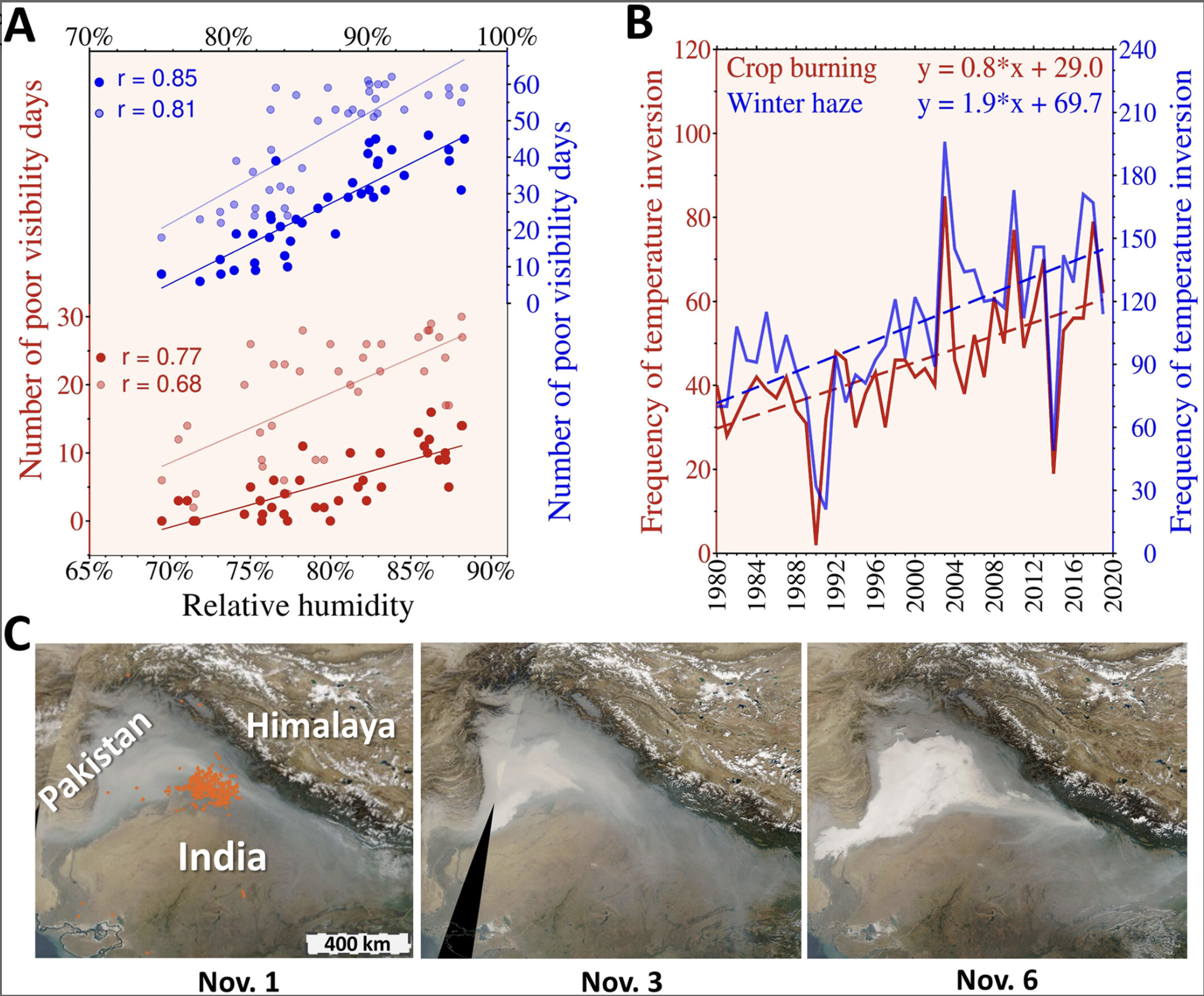
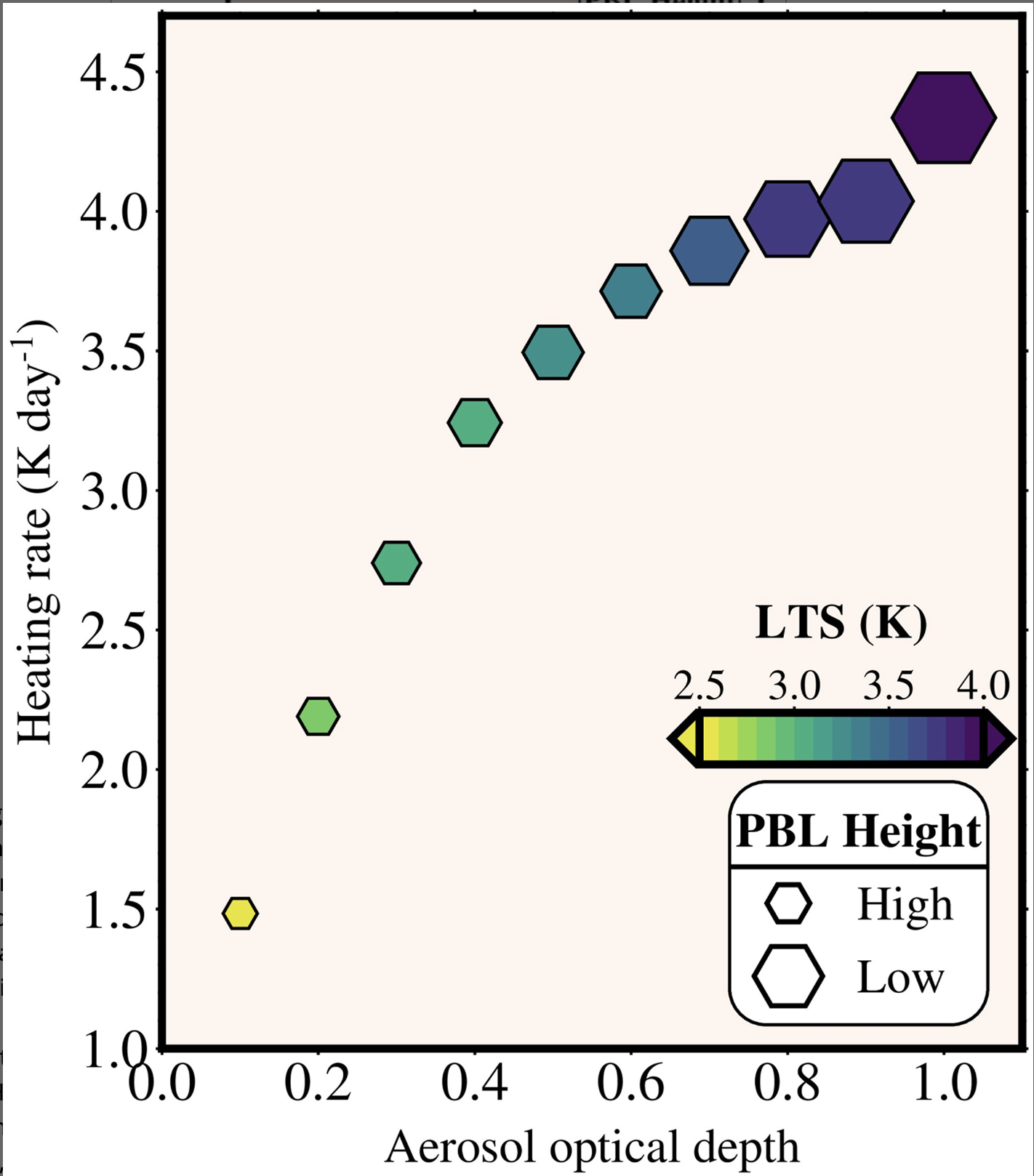
This paper investigates the intensifying smog problem in India, attributing its severity to the rising lower tropospheric stability, which traps pollutants near the surface. The study delves into the aerosol-radiation effects, showing how these interactions further destabilize the atmosphere, leading to even more persistent and dense smog conditions. These findings highlight the critical role of atmospheric dynamics in worsening air quality and emphasize the urgent need for advanced mitigation strategies. This research is pivotal for developing targeted policies and technological solutions to address the growing air pollution crisis in India.
Key Points:
- Increased Atmospheric Stability: Rising lower tropospheric stability is linked to more severe and persistent smog in India due to reduced vertical mixing of pollutants.
- Aerosol-Radiation Effect: Aerosols contribute to smog intensification by altering radiation patterns, trapping heat, and enhancing atmospheric stability.
- Effective air quality management in India must address both emissions and atmospheric conditions, including improved forecasting of meteorological factors and aerosol interactions.
Journal Articles
 Extreme Smog Challenge of India Intensified by Increasing Lower Tropospheric Stability (Contributed equally as first author)Geophysical Research Letters, 2023
Extreme Smog Challenge of India Intensified by Increasing Lower Tropospheric Stability (Contributed equally as first author)Geophysical Research Letters, 2023